Malware threat report
Analysis of CaddyWiper – Wiper Targeting Ukraine
Leading up to and after the war broke out in Ukraine, many destructive cyber attacks have been conducted to disrupt the country’s digital infrastructure. This blog post will analyze the latest malware targeting Ukraine.

Malware Execution
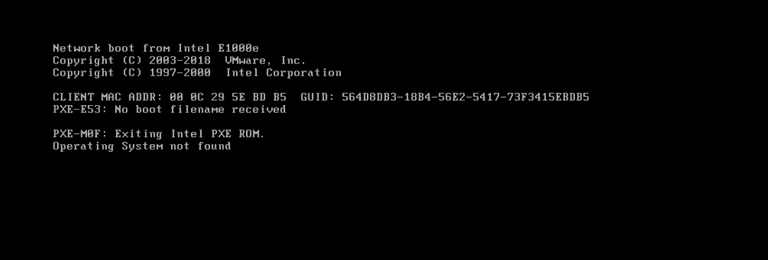
According to the Twitter post by ESET the wiper is deployed by group policy to the infected system. Once run, as administrator, the system will crash and the following screen will be displayed.

Once the computer is rebooted it crashes and will not start anymore and prompt that it cannot locate the operating system.
Static Analysis
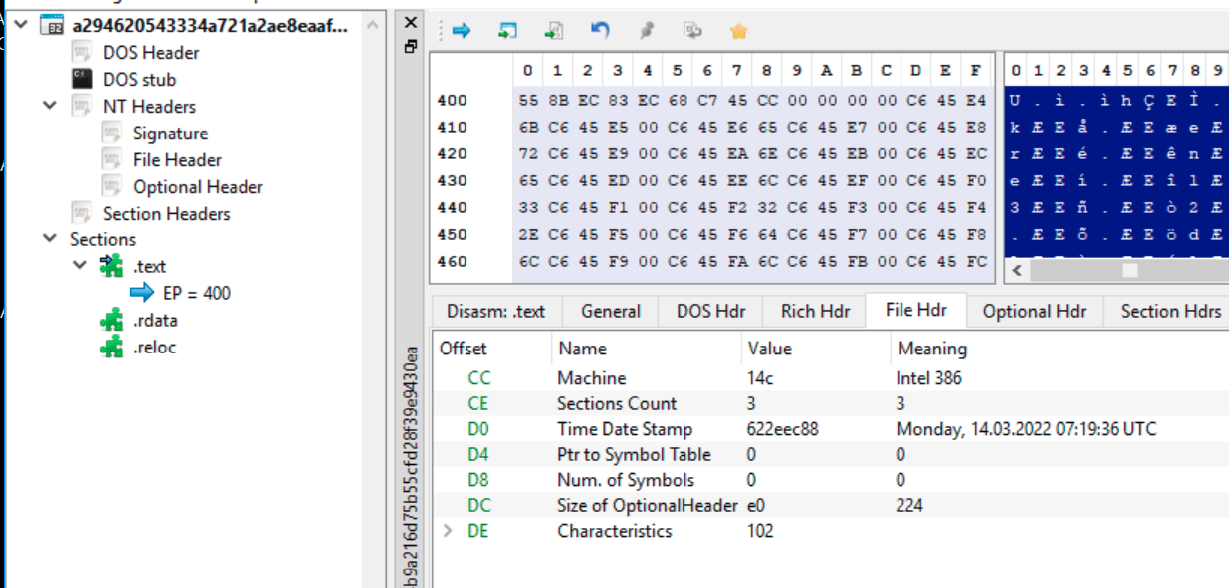
Investigating the time stamp for the sample, it indicates that is compiled on March 14, 2022, showing that it was done just before the attack was conducted.
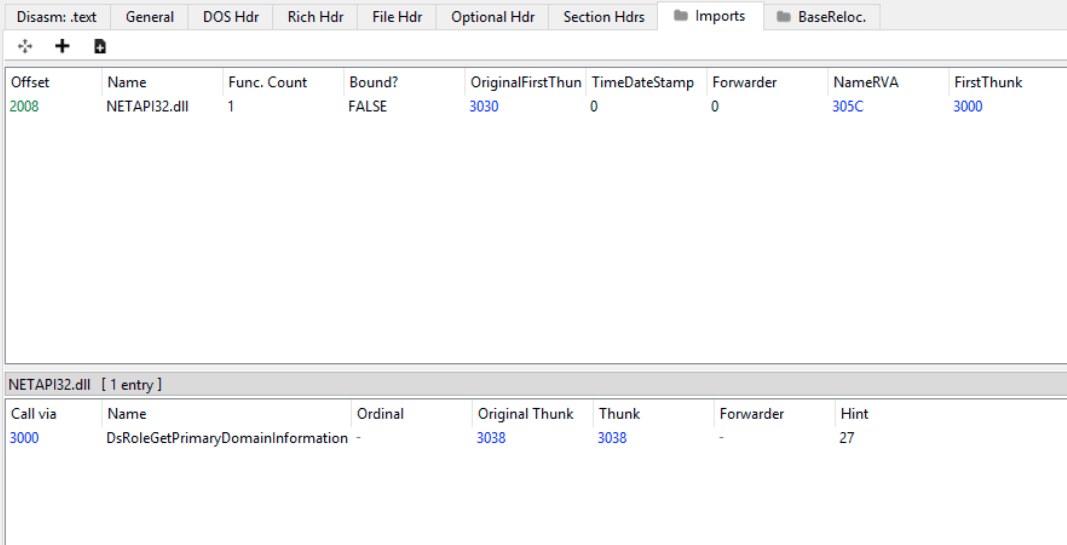
Looking at the Import Address table, there is only one function called, DsRoleGetPrimaryDomainInformation, indicating that there are more functionalities in the malware that are hidden from static tools.
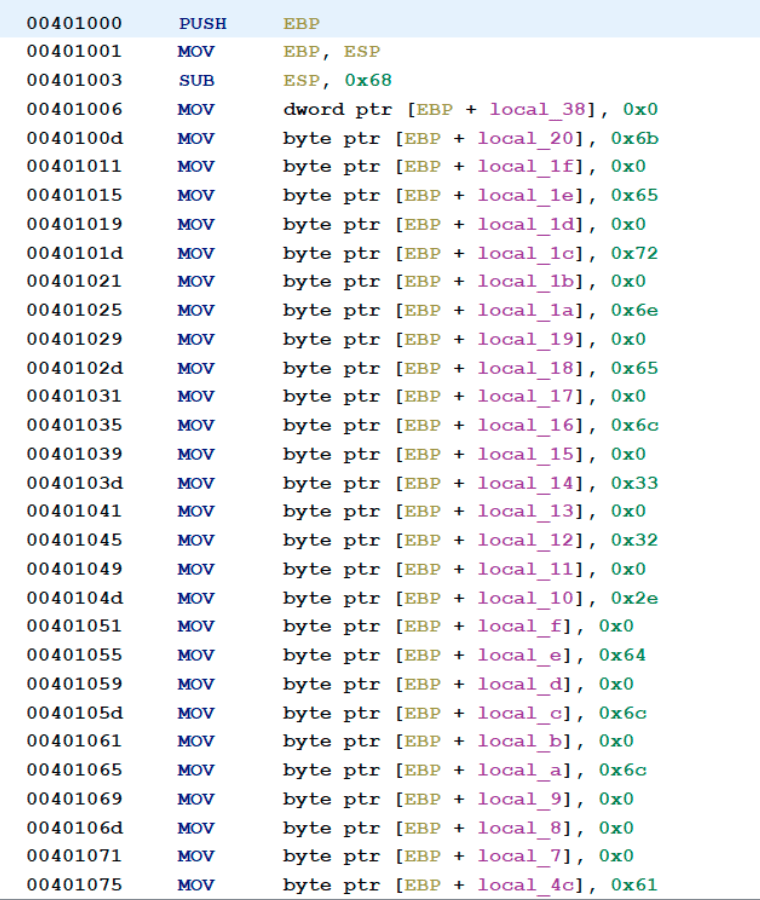
If the sample is opened in a disassembler, in this case Ghidra, it can be seen that it uses a lot of stack strings for obfuscation.
To investigate the stack strings, and reveal what they are hiding, first the tool FLOSS was run on the sample that gave the following output.
FLOSS static ASCII strings !This program cannot be run in DOS mode. Rich% .text `.rdata @.reloc DsRoleGetPrimaryDomainInformation NETAPI32.dll FLOSS static Unicode strings jjjjjjjj0040113A jjjjjj FLOSS decoded 13 strings C:Users C:Users* FindFirstFileA kernel32.dll D:\ D:\* WriteFile advapi32.dll SetEntriesInAclA LookupPrivilegeValueA DeviceIoControl CreateFileW Wkernel32.dll FLOSS extracted 38 stackstrings C:Users netapi32.dll kernel32.dll advapi32.dll CreateFileA kernel32.dll FindFirstFileA OpenProcessToken CreateFileW AdjustTokenPrivileges Wkernel32.dll FreeSid SetEntriesInAclA AllocateAndInitializeSid LocalFree SetFilePointer LookupPrivilegeValueA LocalAlloc LoadLibraryA GetLastError advapi32.dll FindClose kernel32.dll DeviceIoControl CloseHandle CloseHandle kernel32.dll CloseHandle SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege advapi32.dll \.PHYSICALDRIVE9 kernel32.dll LocalFree FindNextFileA GetFileSize GetCurrentProcess WriteFile SetNamedSecurityInfoA
To give context for the stacked strings the tool CAPA was used to find the different locations in the code where stacked strings are used.
contain obfuscated stackstrings (8 matches) namespace anti-analysis/obfuscation/string/stackstring scope basic block matches 0x401000 0x40114A 0x4011D0 0x401750 0x401A10 0x402025 0x40215E 0x4022A0
To get an overview of the intent of each function in relation to where the different stack strings are used for obfuscation, API calls and libraries are mapped to every function that CAPA found in the sample.
0x401000 kernel32.dll, advapi32.dll, LoadLibraryA, netapi32.dll 0x40114A netapi32.dll, netapi32.dll 0x4011D0 DeviceIoControl, kernel32.dll, CreateFileW, CloseHandle, \.PHYSICALDRIVE9 0x401750 advapi32.dll, LookupPrivilegeValueA, AdjustTokenPrivileges, GetLastErrorc 0x401A10 advapi32.dll, SetEntriesInAclA, AllocateAndInitializeSid, SetNamedSecurityInfoA, kernel32.dll, GetCurrentProcess, OpenProcessToken 0x402025 SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege, FreeSid, LocalFree, CloseHandle 0x40215E FreeSid, LocalFree, CloseHandle 0x4022A0 FindFirstFileA, kernel32.dll, FindNextFileA, CreateFileA, GetFileSize, LocalAlloc, SetFilePointer, WriteFile, LocalFree, CloseHandle, FindClose
Execution Flow
Upon start the wiper uses the API call DsRoleGetPrimaryDomainInformation to check if the computer is the primary domain controller by comparing to the hard coded value 0x5, that comes from the struct DSROLE_MACHINE_ROLE. If it is the primary domain controller it will exit. This is probably done because the threat actor is using the domain controller as the source of distribution of the wiper and not to ruin its own foothold.

The next part of the wiper is the file destruction part. It calls the function 0x4022A0 that iterates over the files, using the API calls that are resolved from the stack strings, and writes over the first 0xA00000 bytes with zeros.

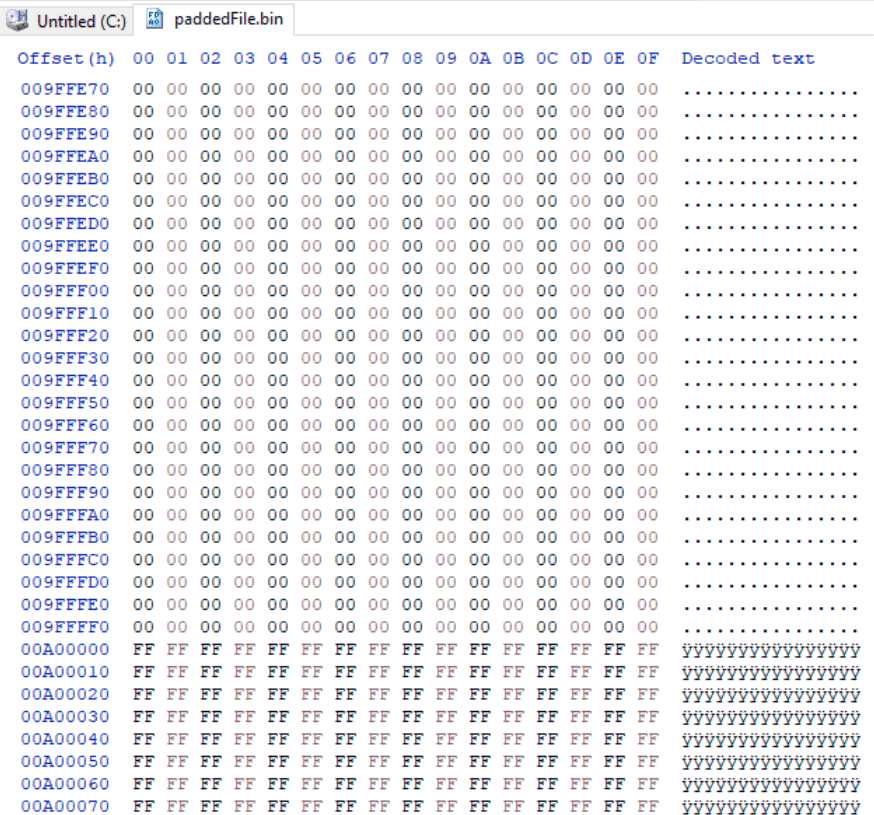
Then the wiper loops through the alphabet (0x18), starting with D all the way up to Z and then one additional iteration, and applies the data destruction from the function in 0x4022A0 to the files in every partition it finds.
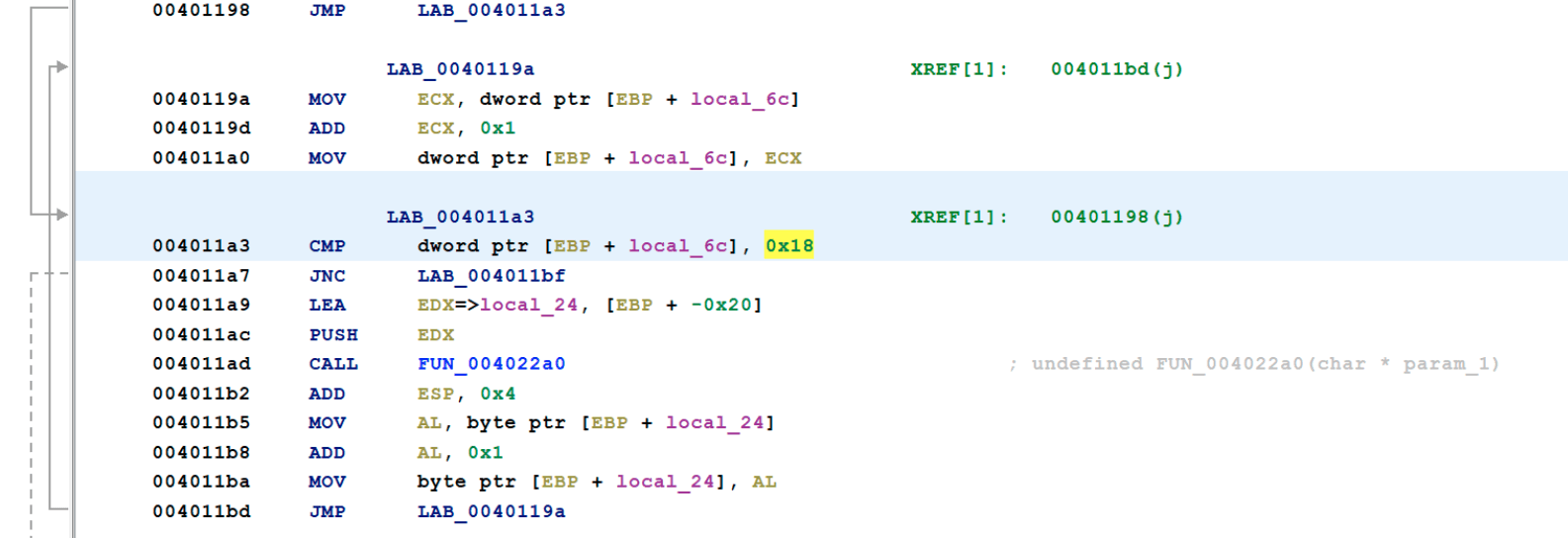
This is the last iteration and has gone past Z to Z+1.
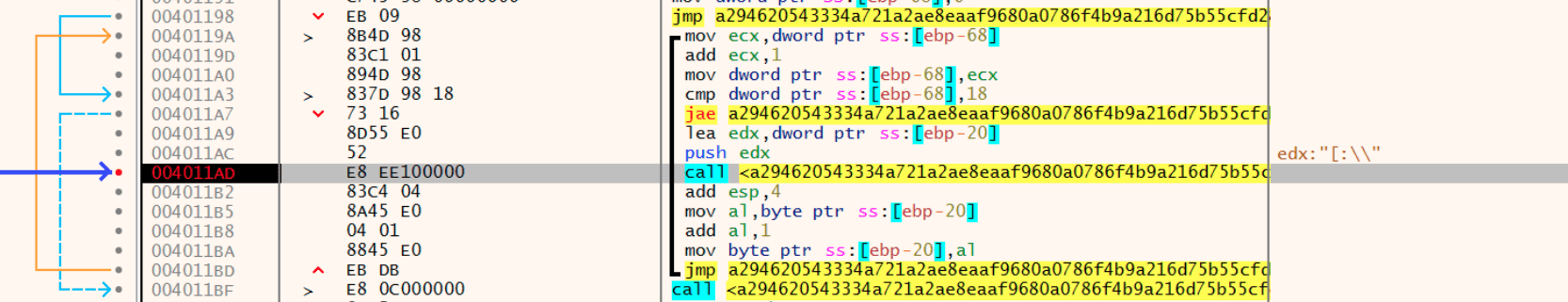
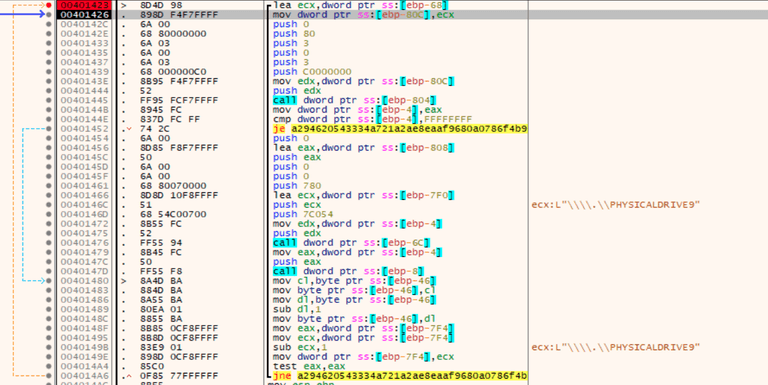
Lastly the wiper loops through a list of open raw access to \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE9 – \\.\PHYSICALDRIVE0 and writing to it using IOCTL_DISK_SET_DRIVE_LAYOUT_EX (0x7c054) by using the API DeviceIoControl. By doing so it erases the Master Boot Record.
Detection
Since the wiper is using stack strings for obfuscation of the part that interacts with the disk, that part can be used as Yara rule for detection.
rule caddy_wiper {
meta:
description = "Search for caddy wiper"
author = "Truesec"
reference = "truesec.se"
date = "2022-03-14"
hash1 = "a294620543334a721a2ae8eaaf9680a0786f4b9a216d75b55cfd28f39e9430ea"
strings:
$x1 = {c6 45 ?? 5c c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 5c c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 2e c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 5c c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 50 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 48 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 59 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 53 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 49 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 43 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 41 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 4c c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 44 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 52 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 49 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 56 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 45} //Stack strings for \.PHYSICALDRIVE
$x2 = {c6 45 ?? 44 c6 45 ?? 65 c6 45 ?? 76 c6 45 ?? 69 c6 45 ?? 63 c6 45 ?? 65 c6 45 ?? 49 c6 45 ?? 6f c6 45 ?? 43 c6 45 ?? 6f c6 45 ?? 6e c6 45 ?? 74 c6 45 ?? 72 c6 45 ?? 6f c6 45 ?? 6c c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 6b c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 65 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 72 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 6e c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 65 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 6c c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 33 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 32 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 2e c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 64 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 6c c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 6c c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 00 c6 45 ?? 43 c6 45 ?? 72 c6 45 ?? 65 c6 45 ?? 61 c6 45 ?? 74 c6 45 ?? 65 c6 45 ?? 46 c6 45 ?? 69 c6 45 ?? 6c c6 45 ?? 65 c6 45 ?? 57} //Stack strings for DeviceIoControl, kernel32.dll, CreateFileW
$a1 = {c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 61 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 64 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 76 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 61 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 70 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 69 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 33 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 32 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 2e c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 64 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 6c c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 6c c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? fe ff ff 00 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 53 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 65 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 74 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 45 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 6e c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 74 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 72 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 69 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 65 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 73 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 49 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 6e c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 41 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 63 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 6c c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 41} //Stack strings for advapi32.dll SetEntriesinAclA
$a2 = {c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 41 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 6c c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 6c c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 6f c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 63 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 61 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 74 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 65 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 41 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 6e c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 64 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 49 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 6e c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 69 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 74 c6 85 ?? ff ff ff 69 c6 45 ?? 61 c6 45 ?? 6c c6 45 ?? 69 c6 45 ?? 7a c6 45 ?? 65 c6 45 ?? 53 c6 45 ?? 69 c6 45 ?? 64} //Stack strings for AllocateAndInitializeSid
condition:
uint16(0) == 0x5A4D
and any of ($x*)
or all of ($a*) and filesize < 50000
}
Stay ahead with cyber insights
Newsletter
Stay ahead in cybersecurity! Sign up for Truesec’s newsletter to receive the latest insights, expert tips, and industry news directly to your inbox. Join our community of professionals and stay informed about emerging threats, best practices, and exclusive updates from Truesec.